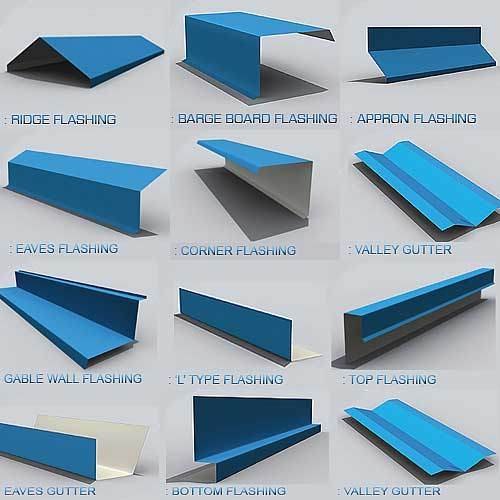
All Types of Flashings
Flashings are essential components in building construction designed to prevent water penetration, protect against moisture, and ensure the integrity of various structural elements. Here are some common types of flashings:
1.Ridge Flashing:Purpose: Installed at the highest point of a roof (ridge) to prevent water penetration.
2.Barge Board Flashing:Purpose: Protects the barge boards (the boards covering the projecting gables) from water.
3.Apron Flashing:Purpose: Used around chimney bases or other vertical structures to divert water away.
4.Eaves Flashing:Purpose: Installed along the eaves to protect against wind-driven rain and ice dams.
5.Corner Flashing:Purpose: Seals corners of structures to prevent water infiltration.
6.Valley Gutter:Purpose: Channels water from roof valleys into gutters, preventing water accumulation.
7.Gable Wall Flashing:Purpose: Protects the joint between a gable wall and the roof.
8.L Type Flashing:Purpose: Used to seal joints, typically at corners or intersections.
9.Top Flashing:Purpose: Installed at the top of a structure, preventing water from entering the building.
10.Bottom Flashing: –Purpose: Seals the bottom edge of a structure, preventing water from infiltrating from below.
GI Angles (Galvanized Iron Angles):
Description:
- Purpose:GI angles are L-shaped structural elements commonly used in construction to provide support and stability at corners and joints.
- Material:Made from Galvanized Iron, where the iron is coated with a layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance.


Gutter-Down Take Pipes
Description: Gutter-down take pipes, commonly referred to as downspouts or drainpipes, are essential components of a building’s rainwater management system.
Function: Designed to channel rainwater efficiently from the gutter system down to the ground or a designated drainage area.
Materials: Made from PVC, aluminium, galvanized steel, or other corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability and longevity.
Industrial Louvers
Description: Industrial louvers are designed to allow or restrict the flow of air and light while providing protection from environmental elements. These louvers are widely used in industrial buildings, commercial structures and various ventilation systems.
Advantages:
- Airflow Control:
- Weather Protection:
- Architectural Aesthetics:
- Customization:
Materials: Commonly constructed from materials such as aluminium, steel, or other durable alloys, & FRP chosen for their strength and resistance to environmental factors.
